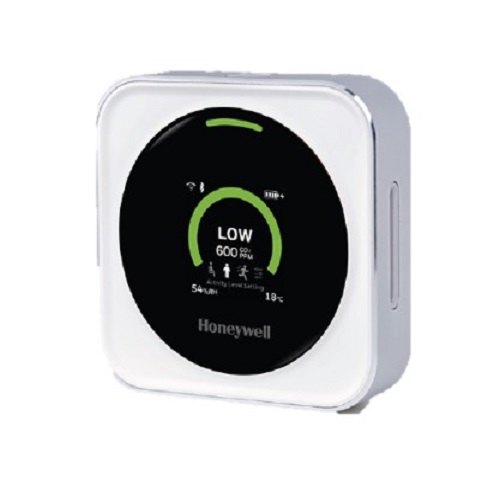
CO2 Monitor
Honeywell Transmission Risk Air Monitor (HTRAM)
A cost-effective CO2 monitor for use in schools, restaurants, gyms and other small-to-medium sized buildings that alerts users when conditions are present that may increase the risk of exposure to airborne viral transmission, including COVID-19. Includes in-built smart algorithm to account for human activity levels in an indoor area, providing a more accurate reading.
The discrete portable monitor is used to continuously check the levels of CO2 in an indoor environment. Research has shown that real-time monitoring of indoor ambient air can be an indicator of increased risk of airborne viral transmission. Using a traffic light system the Transmission Risk Air Monitor will flash when there is elevated levels of CO2 guided by size of room, number of people in that room, breathing rate and duration.
Recommended preventative actions can then be taken including opening windows, turning on HVAC fan, reduce activities or move out of the room depending on the severity of increased levels. Include a CO2 monitor as part of your on-going covid-safe plan to provide duty of care as a business or provider, and peace of mind to your emplyees, customers and students.
Specifications
| Dimensions (H × W × D) | 80 mm × 80 mm × 22 mm [3.1 in × 3.1 in × 0.87 | |
| Weight | 140g | |
| Housing Material | Aluminum alloy | |
| Input Voltage | 5 V | |
| Battery |
Lithium-ion rechargeable battery (10 hour battery time) |
|
| Operating Temp and Humidity | 0°C to 40°C, 0% RH to 90% RH |
Resources
General
 Honeywell Transmission Risk Air Monitor (HTRAM) Brochure for Business
Honeywell Transmission Risk Air Monitor (HTRAM) Brochure for Business
 Honeywell Transmission Risk Air Monitor (HTRAM) Brochure for Schools
Honeywell Transmission Risk Air Monitor (HTRAM) Brochure for Schools
Datasheets
Applications
Schools
Universities
Gyms
Offices
Waiting Rooms
Doctors clinics
Physiotherapy Rooms
Restaurants
Bars
Cafes
FAQ's
• Research has shown a link between increased CO2 levels and potential exposure to airborne viral transmission.
• Indoor activities, such as dining inside a restaurant or in-person learning in a classroom, may increase the risk of potential exposure to airborne viral transmission more than outdoor activities because there is usually less fresh air in an indoor space. In this case, CO2 levels can be used as a reference point for exhaled air and an indicator of the risk of potential exposure to airborne viral transmission.
• Effective monitoring solutions of CO2 levels, like this air monitor, can alert users when conditions are present that may increase the risk of potential exposure to airborne viral transmission.
• A green display means that conditions are present which indicate a low likelihood of risk of potential exposure to airborne viral transmission, out of the three possible colour alerts.
• A yellow display means that conditions are present which indicate a medium likelihood of risk of potential exposure to airborne viral transmission, out of the three possible color alerts.
- If the display moves from green to yellow, occupants should take action, including but not limited to opening windows and turning on the HVAC fan. The user should determine the appropriate actions for their environment.
• A red display indicates that conditions are present which indicate a high likelihood of risk of potential exposure to airborne viral transmission, out of the three possible colour alerts.
- If the display moves from yellow to red, occupants should take action, including but not limited to ventilating the room immediately, reducing activities, and moving out of the room until the light changes back to green. The user should determine the appropriate actions for their environment.
• Once the user selects the activity level on the device, the monitor switches to the activity-based parts per million (ppm) level threshold on alarm alerts, which are calculated based on variables such as average room size, number of people present, breathing rate, and duration.

